
Know Everything about HSN Code in A Comprehensive Guide
*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
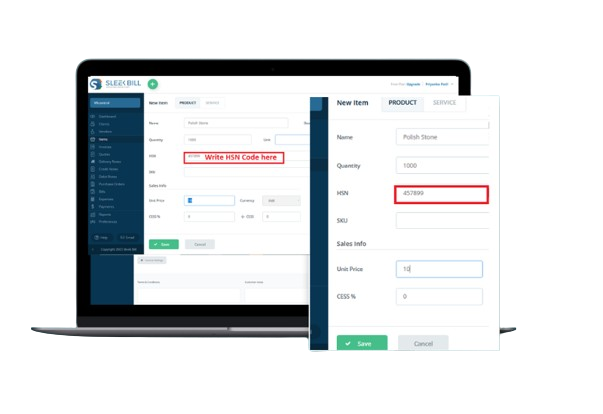
HSN, or Harmonized System of Nomenclature, is a globally recognized system for categorizing goods in international trade. This six-digit uniform code system classifies over 5000 products and is implemented worldwide. Developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO), it has been in effect since 1988, standardizing the classification of goods across countries.
HSN codes play a crucial role in global trade by enabling a standardized system for classifying goods. This uniformity simplified customs procedures, enhanced transparency in international transactions, and facilitated easier identification and categorization of products.
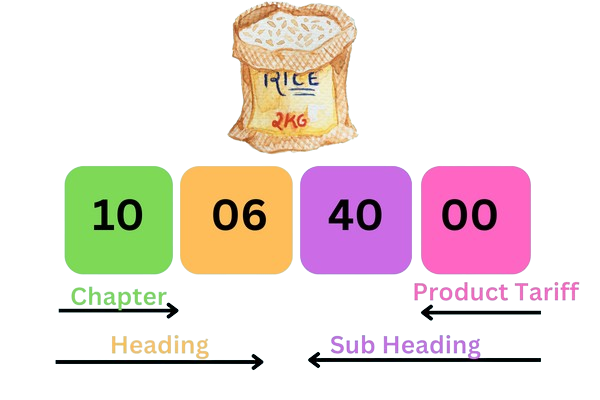
The HSN code consists of 6 digits, where each set of digits represents a specific product category. This structure provides a hierarchical system to classify goods in increasing levels of specificity.

These codes are essential in determining tariff rates, trade statistics, and in the application of GST (Goods and Services Tax) for various products in the trading or business.
HSN codes bring numerous benefits, including:
It helps in aligning with international standards for product classification.
Streamlines the process of import-export by providing a common language for goods.

Aids in accurate GST application and reduces the likelihood of errors in tax computation.
HSN codes are essential for:
For categorizing their products in the supply chain.

To assess and levy the appropriate customs duties on imported and exported goods.

For GST filings and compliance HSN code is essential.
In the context of GST, HSN codes serve a pivotal role:
By using HSN codes, businesses can easily classify their goods as per GST norms, ensuring accurate tax categorization.
The use of HSN codes facilitates smoother tax filing processes, as it provides clear identification of goods for GST purposes.
HSN codes offer a meticulous framework for classifying goods, spanning various industries and categories. Here's an insight into its elaborate structure:
 Sections and Chapters:
Sections and Chapters:
The code encompasses 21 distinct sections, further divided into 99 chapters. These sections and chapters encompass broad categories of goods, providing an initial layer of classification.
 Headings and Subheadings:
Headings and Subheadings:
Within these chapters lie approximately 1,244 headings and 5,224 subheadings. Each heading and subheading narrow down the categorization, offering detailed descriptions of products.
 Logical Progression:
Logical Progression:
The progression from sections to chapters, then to headings and subheadings, ensures a logical flow. This hierarchy allows for an organized and systematic classification.
 Product-Specific Detailing:
Product-Specific Detailing:
The headings and subheadings are where the HSN code becomes particularly specific, detailing individual products and their characteristics.
Seamlessly Adapt to Enhanced HSN Requirements for a Robust GST Framework in India


*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.

Begin by navigating to the e-Way Bill portal. Here, you'll be prompted to enter your unique username and password, followed by the Captcha code. Click on ‘Login’ to access your dashboard and take the first step towards generating your e-Way Bill.

Once logged in, locate the ‘Generate new’ option under the ‘E-waybill’ section on the left-hand side of your dashboard. This will take you to the form where you can start the process of creating a new e-Way Bill.

The generation of an e-Way Bill continues with the completion of critical information on the form

Choose ‘Outward’ if you are the supplier dispatching the consignment. Choose ‘Inward’ if you are on the receiving end of the consignment.

Based on your selection above, pick the correct sub-type that applies to your transaction. This helps in specifying the nature of the consignment more accurately.

Select the type of document that supports your consignment. The options include
Invoice Bill Challan
Credit Note Bill of Entry Others (if the document type is not listed)

Enter the document or invoice number and the date when the document or invoice was issued. This ensures that the e-Way Bill corresponds accurately to the physical shipment.

Fill in the ‘From’ section with your details if you are the supplier. Fill in the ‘To’ section with the recipient's details accordingly fill up the section data.

In this critical section, you'll need to provide comprehensive details about the goods being transported:
Name: Clearly specify the name of the product for identification. Description: Provide a brief description that gives an insight into the specifics of the product, such as model, size, etc. HSN Code:The Harmonized System of Nomenclature code that classifies the goods should be mentioned. This is crucial for tax purposes. Quantity:Indicate the quantity of the goods being shipped.
Unit: Specify the unit of measurement for the quantity mentioned (like kg, liter, unit,Bundle,Barrel etc.). Value/Taxable Value: Declare the value of goods that is subject to tax. Tax Rates: Fill in the applicable tax rates for CGST and SGST or IGST, as per the product classification. Cess:If any cess is applicable, mention the tax rate in percentage.
Before diving into the generation of E Way Bills on Sleek Bill, it's crucial to ensure you have met all prerequisites to facilitate a smooth process. Here's what you need to have in place:
Registration is Key : To initiate any E Way Bill procedures, businesses must first register on the E Way Bill portal. This initial step is a one-time process that grants access to the portal's full range of services.
Transport Specifics : For Road Transport: If the goods are transported by road, you'll need the Transporter ID or the vehicle number. This information is vital to track and manage the consignment during transit.
Documentation on Hand : Ensure you have all necessary documents related to the consignment of goods. This includes having the invoice, bill, or challan readily available, as these are fundamental to the E Way Bill generation process.
Dispute Resolution: Acts as evidence in case of payment or product disputes.
For Rail, Air, or Ship Transport: When transporting goods via rail, air, or ship, you must provide the Transporter ID and have the transport document number, along with the date on the document.

Ease of Doing Business:
HSN codes contribute significantly to simplifying customs procedures, reducing the time and costs associated with international trade.

Compliance and Transparency:
By providing clear guidelines on product classification, HSN codes help businesses comply with various international trade laws and regulations.

Data Analysis and Policy Making:
The standardized system allows for effective tracking and analysis of international trade patterns, assisting policymakers in making informed decisions.
This system of HSN coding helps in the systematic classification of goods under the GST regime and facilitates accurate and uniform documentation across businesses and transactions. It simplifies the process of filing GST returns and ensures compliance with the GST laws.
HSN codes, a pivotal element in international trade, bring a coherent structure to the classification of goods globally. These codes transcend geographical and language barriers, enabling a seamless exchange of goods across borders.
Systematic and Logical Classification:
The primary objective of HSN codes is to categorize goods from around the world methodically. This systematic approach simplifies the process of identifying and classifying a vast array of products under a unified framework.

Simplifying GST Compliance and Filing:
HSN codes significantly simplify the GST filing process. By standardizing the description of goods, HSN codes eliminate the need for detailed product descriptions in tax returns. This leads to a more streamlined and time-efficient process, particularly beneficial as GST returns are largely automated.

Facilitating International Trade:
The uniform classification system of HSN codes aids in streamlining international trade. By using a globally recognized nomenclature, it eases the process of dealing with different customs regulations and trade policies.
Threshold for HSN/SAC Code Declaration in GSTR-1
The requirement to declare HSN/SAC codes in GSTR-1 is based on turnover slabs. This tiered approach ensures that smaller businesses with lower turnover are not overburdened with compliance requirements, while larger businesses maintain detailed and systematic reporting.
The eligibility for declaring HSN codes in GST (Goods and Services Tax) invoices in India is based on the annual aggregate turnover (AATO) of the previous financial year. The requirements for declaring HSN codes have been updated as per the CGST notification 78/2020, dated 15th October 2020, effective from 1st April 2021. Here's a summary of who is eligible and the number of digits of HSN code that need to be declared based on the AATO:

Businesses with an AATO Up to Rs. 5 crore:
● For B2B and B2C tax invoices: Declaring a 4-digit HSN code is mandatory for B2B and optional for B2C.
Businesses with an AATO More than Rs. 5 crore:
● For all types of invoices (B2B and B2C): Declaring a 6-digit HSN code is mandatory.
This system of HSN coding helps in the systematic classification of goods under the GST regime and facilitates accurate and uniform documentation across businesses and transactions. It simplifies the process of filing GST returns and ensures compliance with the GST laws.
Seamlessly Navigate Global Commerce with Sleekbill


*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes are used internationally for the classification of goods. These codes are typically 6 digits long. However, different countries can implement the HSN system to varying extents:

Global Standard
Internationally, HSN codes are usually 6 digits. The system, developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO), classifies goods using these 6 digits, which are standardized across participating countries.

India's Implementation
In India, the HSN codes have been extended to 8 digits to allow for more detailed classification. This expansion is done to incorporate specific descriptions pertinent to goods traded within the country.
This extended format allows for more precise categorization and is useful in aligning with domestic tax laws, including the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India.
India, a member of the World Customs Organization (WCO) since 1971, has adeptly integrated the Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) into its trade and taxation framework.

Initial Adoption
Initially, India adhered to the 6-digit HSN codes for classifying commodities, aligning with the global standard set by the WCO and also suitable for GST System.
Enhanced Precision
To enhance the precision of commodity classification, India's Customs and Central Excise departments expanded the HSN codes by adding two additional digits.

8-Digit Classification
This augmentation transformed the standard 6-digit HSN codes into a more detailed 8-digit classification system, tailored to meet India's specific requirements in trade and taxation.
India's adoption and adaptation of the HSN code system reflect its commitment to aligning with global trade practices while catering to domestic needs. The 8-digit HSN codes not only facilitate international trade but also ensure greater accuracy in tax and customs administration within the country.
Animals
Meat and edible offal
Fish, molluscs, crustaceans, and other aquatic invertebrates
Dairy produce, birds' eggs, honey and other edible products of animal origin that are not specified elsewhere.
Other products of animal origin that are not specified elsewhere.
Live trees and plants, bulbs, roots, etc., cut flowers and ornamental foliage
Edible vegetables, certain roots and tubers
Edible fruit and nuts, the peel of citrus fruits or melons.
Tea, coffee, mate and spices
Cereals
Milling products, malt, wheat gluten, starches, and inulin
Oil seeds and oleaginous fruits, grains, straw and fodder, seeds and fruit, and industrial or medicinal plants
Lac, gum, resin, and other saps and extracts
Vegetable plaiting materials, and vegetable products that are not specified elsewhere
Animal or vegetable oils, their cleavage products, waxes, and prepared edible fats
Preparation of meat, fish or crustaceans, molluscs, or any other aquatic invertebrates
Sugar and sugar confectionery
Cocoa and cocoa preparations
Preparations of cereals, starch, flour, milk, and pastry products
Preparation of vegetables, fruits, nuts, or plant parts
Miscellaneous edible preparations
Beverages, vinegar, and spirits
Residue and food waste, prepared animal fodder
Tobacco and tobacco substitutes that are manufactured
Salt, earths and stones, sulphur, plastering material, lime, and cement
Ores, slag, and ash
Mineral fuel, mineral oils and products of their distillation, mineral waxes, and bituminous substances.
Inorganic chemicals, organic or inorganic compounds of precious metals, rare-earth metals, radioactive elements, or isotopes.
Organic chemicals
Pharmaceutical products
Fertilizers
Tanning or dyeing extracts, tannins and their derivatives, dyes, pigments, and other colouring matter, varnishes and paints, inks, putty and other mastics
Essential oils and resinoids, cosmetic or toilet preparations, perfumery
Soap, washing preparations, organic surface-active agents, lubricating preparations, prepared waxes, artificial waxes, polishing or scouring preparations, candles and similar items, modelling pastes, dental preparations and dental waxes with a basis of plaster
Albuminoidal substances, glues, enzymes, and modified starches.
Explosives, pyrotechnic products, pyrophoric alloys, certain combustible preparations, and matches.
Photographic or cinematographic goods.
Miscellaneous chemical products
Plastics and plastic articles
Rubber and rubber articles
Raw hides and skins (other than furskins) and leather
Articles made of leather, travel goods, handbags and similar containers, saddlery and harnesses, articles made of animal gut (other than silkworm gut).
Furskins and artificial fur and articles thereof
Wood and wooden articles, wood charcoal.
Cork and articles of cork.
Cork and articles of cork.
Pulp of wood or other fibrous cellulosic material, recovered paper or paperboard (waste and scrap)
Paper and paperboard, articles made of paper pulp, or articles made of paper or paperboard.
Printed books, pictures, newspapers, and other products of the printing industry, typescripts, manuscripts, and plans
Silk
Wool, fine or coarse animal hair, horse hair yarn and other woven fabrics
Cotton
Other vegetable textile fibres, paper yarn and woven farics made of paper yarn
Man-made filaments
Man-made staple fibres
Wadding, felt and nonwovens, twine, cordage, special yarns, ropes, and cables and articles thereof
Carpets and textile floor coverings
Special woven fabrics, lace tapestries, tufted textile fabrics, trimmings, and embroidery
Impregnated, covered, coated, or laminated textile fabrics, textile articles made for industrial use.
Knitted or crocheted fabrics
Articles of apparel and clothing accessories that are knitted or crocheted
.Articles of apparel and clothing accessories that are not knitted or crocheted
Other made up textile articles, sets, worn clothing and textile articles, and rags
Footwear, gaiters, etc., and the parts of such articles
Headgear and parts thereof
Umbrellas and sun umbrellas, walking sticks, seat sticks, riding crops and parts thereof, and whips
Prepared feathers and down and articles made thereof, artificial flowers, and articles made of human hair.
Articles made of stone, plaster, cement, asbestos, mica or similar materials
Ceramic products
Glass and glassware
Natural or cultured pearls, precious metals, metals that are clad with precious metal and articles thereof, precious or semi-precious stones, imitation jewellery, coins.
Iron and steel
Articles made of iron or steel
Copper and articles thereof
Nickel and articles thereof
Aluminium and articles thereof
(Reserved for possible future use)
Lead and articles thereof
Zinc and articles thereof
Tin and articles thereof
Other base metals, cermets, and articles thereof
Tools, implements, spoons and forks, cutlery, of base metal, and parts thereof
Miscellaneous articles made of base metal
Nuclear reactors, machinery and mechanical appliances, boilers, and parts thereof
Electrical machinery and equipment and parts thereof, sound reproducers and recorders, television image and sound reproducers and recorders, and parts and accessories of such articles
Tramway or railway locomotives, tramway or railway track fixtures and fittings and parts thereof, rolling stock and parts thereof, mechanical (including electro-mechanical) traffic signalling equipment of all kinds.
Vehicles other than tramway or railway rolling stock, and parts and accessories thereof
Aircraft, spacecrafts, and parts thereof
Ships, boats and floating structures
Optical, photographic, cinematographic, checking, measuring, precision, medical or surgical instruments and apparatus, parts and accessories thereof.
Clocks and watches and parts there of
Musical instruments, and parts and accessories of such articles.
Arms and ammunition, parts and accessories thereof
Furniture, mattresses, mattress supports, bedding, cushions and similar stuffed furnishing, lamps and lighting fittings, which are not elsewhere specified or included, illuminated signs and name-plates and the like, prefabricated buildings
Toys, games and sports requisites, parts and accessories thereof
Miscellaneous manufactured articles
Works of art, collectors' pieces and antiques
Project imports, laboratory chemicals, personal imports by air or post, passenger's baggage, ship stores.
Services
Mastering the Complex World of HSN Codes for Consistent and Accurate Classification.


*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
HSN code, a globally standardized system, is integral in streamlining the classification of goods in international trade. It encompasses approximately 5,000 commodity groups, each uniquely identifiable through a six-digit code. The structure of HSN codes is both legal and logical, ensuring consistency and clarity in global commerce.
The GST regime in India has revised the HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code declaration requirements for tax invoices. These changes, effective from April 1, 2021, aim to bring more clarity and standardization in tax invoices under GST, especially for B2B and B2C transactions.
Each product category is assigned a distinct six-digit code, facilitating easy identification and categorization of commodities worldwide.
 For Businesses with Annual Turnover up to ₹5 Crore:
For Businesses with Annual Turnover up to ₹5 Crore: ● Type of Invoice: B2B Tax Invoices
● HSN Code Digits Required: 4 digits (Mandatory)
● Type of Invoice: B2C Tax Invoices
● HSN Code Digits Required: 4 digits (Optional)
 For Businesses with Annual Turnover More Than ₹5 Crore:
For Businesses with Annual Turnover More Than ₹5 Crore: ● Type of Invoice: All Invoices (Both B2B and B2C)
● HSN Code Digits Required: 6 digits (Mandatory)
 Special Case for Exports and Imports
Special Case for Exports and Imports ● HSN Code Requirement: Mandatory 8 digits of HSN code for all export and import transactions under GST.
 Reference Period for Turnover Calculation
Reference Period for Turnover Calculation ● Annual Aggregate Turnover: For reporting invoices in the financial year 2021-22, the turnover of the previous financial year, i.e., FY 2020-21, should be referred to.
 Implication for Businesses
Implication for Businesses Every tax invoice issued by the taxpayer under GST must now include the specified HSN codes as per these guidelines. This ensures uniformity and compliance across all scales of business operations.
Adding HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes in the GST (Goods and Services Tax) portal is a straightforward process. Here's a step-by-step guide to assist you:
1 Login to GST Portal: Access the official GST portal (www.gst.gov.in) and log in with your credentials.
2 Navigate to Registration Amendment: On the dashboard, select ‘Services’, then choose ‘Registration’, and proceed to ‘Amendment of Registration Non-core fields’.
3 Access Goods and Services Tab: Once in the amendment section, click on the ‘Goods and Services’ tab.
4 Select the Goods Tab: Within the Goods and Services section, click on the ‘Goods’ tab if you're adding HSN codes for goods. For services, select the ‘Services’ tab.
5 Search and Add HSN Code: In the Goods section, you can search for the relevant HSN chapter by entering either the HSN code or the name of the item. Ensure you choose the correct HSN code as it's crucial for accurate GST filing.
6 Save the Information: After selecting the appropriate HSN code, click on ‘Save and continue’. Keep clicking the ‘Save’ button at each step until you reach the verification step.
7 Complete Verification and Submission:
7.1 EVC (Electronic Verification Code): This method is recognized by the income tax department for most types of individual taxpayers. It involves receiving a code on the registered mobile number which is then used for verification.
7.2 DSC (Digital Signature Certificate): This is an electronic signature, issued by a certifying authority, used to verify the identity of the taxpayer. It’s generally used by companies and LLPs.
8 Final Submission: After completing the verification process using either DSC or EVC, submit the amendment. Once submitted, the changes will be reflected in your GST registration details.
Remember, it's important to choose the correct HSN code corresponding to your goods or services as it affects the GST rate applicable to your items and ensures compliance with GST laws.