
Navigating the Ins and Outs of Goods and Services Tax Returns for Smooth Compliance.
*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
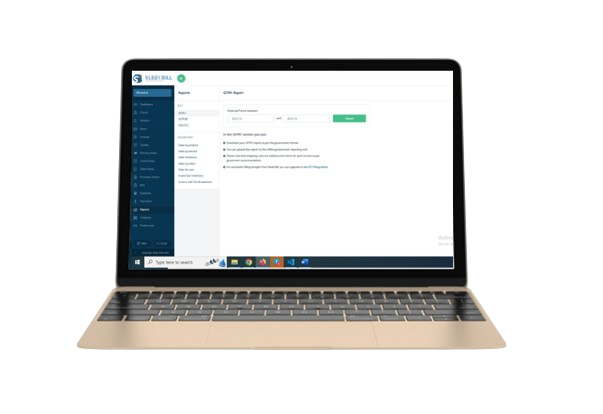
Understanding GST Returns is crucial for maintaining tax compliance and financial accuracy in your business operations. A GST Return is a legally mandated document that encapsulates the details of a taxpayer's income/sales and expenses/purchases. It's essential for every gistered entity (identified by a GSTIN) to accurately file these returns, as they enable tax authorities to ascertain the net tax liability effectively.

● Purchases: Documenting all the goods and services purchased.
● Sales: Reporting all the revenue generated from sales.
● Output GST: Calculating the GST levied on sales.
● Input Tax Credit: Detailing the GST paid on purchases, which can be offset against the GST liability on sales.

● GSTR-1: Details of outward supplies of taxable goods and services.
● GSTR-2A: Reflects inward supplies, auto-populated from the sellers' GSTR-1.
● GSTR-3B: A summary of outward supplies, Input Tax Credit claimed, and tax payable.
● GSTR-9: The annual return, consolidating the details provided in the monthly/quarterly returns.
● Monthly Filings: Typically required for businesses with higher turnover.
● Quarterly Filings: Suitable for smaller businesses under the QRMP scheme.
● Annual Filings: Mandatory for all Registered entities in GST.
● Data Reconciliation: Aligning data across GSTR-1, GSTR-2A, and GSTR-3B.
● Deadline Adherence: Keeping track of various filing deadlines.
● Accuracy in Reporting: Ensuring error-free and consistent data reporting.
It helps in the precise calculation of the tax liability.
Enables the process of seeking reimbursements for any surplus GST payments made.
Ensures compliance with tax laws and maintains transparency in business operations.
Acts as a comprehensive record of financial transactions for audit and analysis.
Incorporating GST-compliant software like Sleek Bill can significantly streamline the process of GST return filing. It offers features like automated data entry, error-checking mechanisms, and timely reminders for deadlines, thereby reducing manual efforts and enhancing accuracy.
Navigating the GST landscape can be complex, but understanding who is required to file GST returns is crucial for compliance. Here's a breakdown of the entities and their filing obligations:
 Regular Businesses with Substantial Turnover:
Regular Businesses with Substantial Turnover: ● Businesses with an annual aggregate turnover (AATO) of more than Rs. 5 crores are required to file GST returns.
● This segment faces a comprehensive filing requirement, amounting to 25 returns annually.
 Taxpayers Outside QRMP Scheme:
Taxpayers Outside QRMP Scheme: ● Entities not opting for the Quarterly Return Filing and Monthly Payment of Taxes (QRMP) scheme must file two monthly returns.
● This scenario presents a significant filing responsibility, necessitating diligence and accuracy in record-keeping.
 Special Cases – Composition Dealers and Others:
Special Cases – Composition Dealers and Others: ● There are different filing requirements for special categories like composition dealers.
● These entities have unique return forms and filing frequencies, tailored to their simplified tax regime.
 QRMP Scheme Filers:
QRMP Scheme Filers: ● Taxpayers under the QRMP scheme file fewer returns, totaling 9 each year.
● This includes 4 GSTR-1 and 4 GSTR-3B returns, along with one annual return.
● Despite quarterly filing, QRMP taxpayers are required to pay taxes monthly, demanding consistent financial management.
 Importance of Knowing Your Category
Importance of Knowing Your Category ● Compliance: Understanding which category, you fall under is essential for meeting statutory obligations and avoiding penalties.
● Financial Planning: Regular and QRMP filers must plan their cash flows differently, considering their distinct tax payment schedules.
● Record Maintenance: The frequency of filing impacts how businesses maintain and process their transaction records.
Effortlessly Navigate Tax Compliance with Sleek Bill's Advanced GST Return Solutions for a Seamless and Hassle-Free Experience


*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
Understanding the Spectrum of GST Returns The Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India encompasses a variety of returns, each catering to specific taxpayer categories and transaction types.


● The GST regime includes 13 different returns:
GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, GSTR-4, GSTR-5, GSTR-5A, GSTR-6, GSTR-7, GSTR-8, GSTR-9, GSTR-10, GSTR-11, CMP-08, and ITC-04.
● Each return serves a unique purpose, addressing various aspects of GST compliance.
● Not all returns apply universally to every taxpayer.
● Returns are filed based on the type of taxpayer or the registration obtained under GST.
● Taxpayers with a turnover exceeding Rs. 5 crore are required to file a self-certified reconciliation statement in Form GSTR-9C.
● GSTR-2A (dynamic) and GSTR-2B (static) are two key statements available to taxpayers for managing input tax credits.
● The Invoice Furnishing Facility (IFF) under the QRMP scheme allows small taxpayers to furnish their B2B sales for the first two months of the quarter.
● Despite the quarterly return filing, monthly tax payments are mandatory, facilitated through Form PMT-06.
● Compliance:
Matching your business profile with the correct return type is crucial for meeting GST obligations.
● Efficiency:
Understanding which returns apply to your business can streamline the filing process and reduce compliance costs.
Navigating through the myriad of GST returns can be a complex task. Here’s a simplified guide to the various types of GST returns and their respective due dates:
| GST Return | Description | Frequency | Due Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| GSTR-1 | Details of outward supplies of taxable goods/services. | Monthly/Quarterly (QRMP scheme). | 11th of next month (Monthly), 13th of the month following the quarter (Quarterly). |
| IFF | Details of B2B supplies for QRMP scheme taxpayers. | Monthly (first two months of the quarter). | 13th of the following month. |
| GSTR-3B | Summary of outward supplies, input tax credit, and tax payment. | Monthly/Quarterly. | 20th of next month (Monthly), 22nd or 24th of the month following the quarter (Quarterly). |
| CMP-08 | Summary of outward supplies, input tax credit, and tax payment. | Monthly/Quarterly. | 18th of the month following the quarter. |
| GSTR-4 | Annual return for Composition Scheme taxpayers. | Annually. | 30th of the month following the financial year. |
| GSTR-5 | Return for non-resident taxable persons. | Monthly. | 20th of the next month. |
| GSTR-5A | Return for non-resident OIDAR service providers. | Monthly. | 20th of the next month |
| GSTR-6 | Return for an input service distributor to distribute the eligible input tax credit to its branches. | Monthly. | 13th of the next month. |
| GSTR-7 | Return to be filed by registered persons deducting tax at source (TDS). | Monthly. | 10th of the next month. |
| GSTR-8 | Return to be filed by e-commerce operators containing details of supplies effected and the amount of tax collected at source by them. | Monthly. | 10th of the next month. |
| GSTR-9 | Annual return by a regular taxpayer. | Annually | 31st December of the next financial year. |
| GSTR-9C | Self-certified reconciliation statement. | Annually | 31st December of the next financial year. |
| GSTR-10 | Final return to be filed by a taxpayer whose GST registration is cancelled. | Once, upon cancellation of registration. | Within three months of the date of cancellation or date of cancellation order, whichever is later. |
| GSTR-11 | Details of inward supplies to be furnished by a person having UIN and claiming a refund. | Monthly | 28th of the month following the month for which the statement is filed. |
| ITC-04: Statement for Principal/Job- Worker Transactions | Statement to be filed by a principal/job- worker about details of goods sent to/received from a job-worker. This return is crucial for businesses engaging in job work where goods are sent out for processing or manufacturing and then received back. | Annually: For taxpayers with an Annual Aggregate Turnover (AATO) up to Rs.5 crore. Half-yearly: For taxpayers with an AATO greater than Rs.5 crore. | ● For AATO up to Rs.5 crore: 25th April for the entire financial year. ● For AATO greater than Rs.5 crore: 25th October for the first half of the financial year and 25th April for the second half of the financial year. |

● Prescribed Formats: Each GST return has a specific format, which is crucial for maintaining uniformity and ensuring accurate tax reporting.
● Perceived Complexity: While the process might appear complex, especially for new taxpayers, the GST portal is designed to be user-friendly. Many taxpayers adapt to the system with a bit of practice and guidance.
● GST Portal Submission: All these forms must be filed electronically on the official GST portal. This online submission makes the process more streamlined and accessible.
● Support and Resources: The GST portal offers resources and guides to assist taxpayers in understanding and completing their returns. Additionally, tax professionals and GST software solutions can provide valuable support in this process.
Filing GST returns online ensures transparency, accuracy, and convenience, contributing to a more efficient tax system in India.
 Non-Compliance Penalty:
Non-Compliance Penalty:  Interest Rate:
Interest Rate: Interest Calculation:
Interest Calculation:  Late Fee Charges:
Late Fee Charges: Standard Late Fee: Rs. 100 per day per Act, i.e., Rs. 100 under CGST and Rs. 100 under SGST.
Maximum Late Fee: Rs. 200 per day, capped at Rs. 5,000.
 Revised Late Fee Structure (Post June 2021):
Revised Late Fee Structure (Post June 2021):Nil Tax Liability: Maximum late fee capped at Rs. 250.
Turnover up to Rs. 1.5 Crore: Maximum late fee capped at Rs. 1,000.
Turnover between Rs. 1.5 Crore and Rs. 5 Crore: Maximum late fee capped at Rs. 2,500.
Transform your GST return filing experience with Sleek Bill's precision and ease.


*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
GST returns play a pivotal role in India's tax framework, ensuring compliance and transparency in the financial ecosystem. While the array of returns and their respective deadlines may initially seem daunting, the systematic design of the GST portal simplifies this process. As businesses adapt to this structure, they not only align with legal requirements but also contribute to the nation's economic growth. With resources available for assistance, every taxpayer can master the art of GST filing, paving the way for a more robust and efficient tax system.
Regular Taxpayers GST is generally paid monthly by regular taxpayers, ensuring consistent tax remittance to the government.
Quarterly Returns Option: Taxpayers can opt for quarterly filing of returns under specific schemes, allowing for more manageable tax management for smaller businesses.
Composition Scheme Eligibility:
● For Manufacturers/Dealers: Businesses with an annual aggregate turnover of up to Rs. 1.5 crore can choose the composition scheme.
● For Service Providers: Service providers with an annual turnover of up to Rs. 50 lakh are also eligible for this scheme.
● Quarterly Payment under Composition Scheme: Those opting for the composition scheme are required to file a quarterly statement-cum-challan, facilitating tax payments on a quarterly basis instead of monthly.
This flexibility in the GST payment structure allows businesses of different sizes and types to manage their tax liabilities more effectively, catering to the diverse needs of the Indian business landscape.