
Unlocking the Secrets of GST Invoices: A Step-by-Step Guide for Easy and Comprehensive Understanding
*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
_11zon(1).png)
A GST invoice is more than just a bill; it's a critical document in the GST regime. It's a formal instrument that a seller or service provider issues to their customer, detailing the transaction. This invoice serves as the primary evidence for the supply of goods and services.
The GST invoice comprehensively lists the products or services provided, making it a clear and precise document for both parties involved in the transaction.
It specifies the cost of each item or service before the addition of CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax) and SGST (State Goods and Services Tax), offering transparency in pricing.
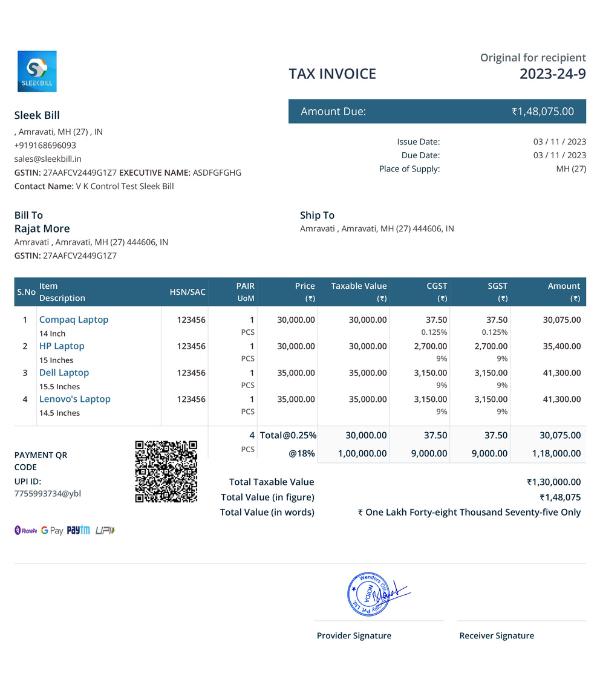
It includes crucial details about the seller and the buyer, such as GSTIN (GST Identification Number), legal name, and address, which are pivotal for tax purposes.

The invoice displays the exact amount of tax levied on each product or service, ensuring clarity in tax calculations and compliance.
The GST invoice plays a vital role in calculating the GST owed by a business. It also enables buyers to claim input tax credit, thereby reducing their tax liability.

Maintaining GST invoices aids in efficient record-keeping, which is essential for compliance with GST regulations and smooth business operations.

Under the GST law, issuing a GST invoice for every sale is mandatory. It's a key document for tax purposes and a legal requirement for businesses.
The detailed breakdown of prices and taxes in the GST invoice helps in resolving disputes and ensures transparency in business transactions.
Under the GST regime, the invoice is more than just a bill; it’s a crucial compliance document. Every GST invoice, whether it's a primary bill, supplementary bill, or a revision, should meticulously include specific details:
 Supplier Information:
Supplier Information:
• GSTIN of the supplier
• Name and address of the supplier issuing the invoice
• Unique serial number (not exceeding 16 digits)
• Date of issue
 Recipient Details:
Recipient Details:
• Name and address of the recipient (if registered)
• Billing and shipping address
 Product or Service Specifics:
Product or Service Specifics:
• Detailed description of goods or services
• HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code for goods or SAC (Services Accounting Code) for services
 Financial Details:
Financial Details:
• Invoice value
• Rate and amount of CGST, SGST, and IGST
• Applicable discounts
• Tax amount (segregated into CGST, SGST, IGST)
• Indication of reverse charge or forward charge mechanism, if applicable
 Authorization:
Authorization:
• Signature of the issuer or an authorized representative.
 Authorization:
Authorization:
The GST invoice should be issued at the time of the supply of goods or services: For goods, it's generally at the time of removal or delivery. For services, it's within a prescribed time after the service is rendered.
 Authorization:
Authorization:
Embracing the GST invoice system is not just about compliance: it's about adopting a more transparent and efficient way of documenting business transactions. With tools like Sleek Bill, managing GST invoices becomes streamlined and hassle-free, ensuring your business stays on top of its financial and legal obligations.
 Authorization:
Authorization:
Explore Sleek Bill for Easy GST Invoicing: Simplify your GST invoicing process with Sleek Bill. Our software ensures accuracy, compliance, and ease of use.
 Authorization:
Authorization:
Stay Compliant with Sleek Bill: With Sleek Bill, ensure that your business adheres to GST regulations effortlessly. Our intuitive interface makes GST billing seamless and straightforward.
Generate Invoice and Stay Compliant – Elevate Your Invoicing Experience Today.


*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
In the realm of GST, the bill format plays a pivotal role. As per Section 2(66) of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act of 2017, understanding the precise structure of a GST bill is crucial for compliance.
Basis: Section 31 of the CGST Act outlines the mandatory requirements for an invoice to be recognized as a valid GST document.
Format Variability: The GST bill can be both electronic and manual, offering flexibility to businesses in how they issue these invoices.
 GSTIN of the supplier and the recipient:
GSTIN of the supplier and the recipient:
 Unique invoice number:
Unique invoice number:
 Description of goods or services.
Description of goods or services.
 Quantity and total value
Quantity and total value
 Taxable value and discounts, if any
Taxable value and discounts, if any
 Rate and amount of taxes (CGST, SGST, IGST)
Rate and amount of taxes (CGST, SGST, IGST)
 Place of supply and shipping address.
Place of supply and shipping address.
 Signature of the supplier.
Signature of the supplier.

Offer convenience, accuracy, and are environmentally friendly. They can be integrated with accounting software for automated record-keeping.
Traditional method, suitable for small-scale businesses or in areas with limited digital infrastructure.
Sleek Bill simplifies the creation of GST-compliant invoices, ensuring that all necessary details are accurately captured.

With Sleek Bill, transition smoothly from manual to electronic invoicing, harnessing the power of digital efficiency.
![]()
Invoice Copies Required: ● Two Copies Mandate: For services supplied, only two copies of the GST invoice are necessary. ● Distinct Recipients: Each copy serves a specific purpose and recipient.
Allocation of Copies:
● Original Copy: Designated for the recipient of the service. ● Duplicate Copy: Retained by the supplier for internal record-keeping and compliance.
Ensuring Compliance: ● GST Regulations: Aligns with GST invoicing requirements for service supplies. ● Verification and Reconciliation: Facilitates easier verification and reconciliation during GST audits and filings.
Streamlining Record-Keeping: ● Organized Documentation: Helps in organizing financial records systematically. ● Ease of Access: Ensures easy retrieval of service transaction records for future reference or audits.
Original Invoice for Service Recipient: ● Purpose: Acts as proof of service provided and the basis for payment. ● Details Included: Contains all relevant service details, including description, charges, and GST information.
Duplicate Invoice for Supplier: ● Internal Use: Essential for maintaining financial and tax records. ● Audit and Compliance: Assists in tax filings, audits, and tracking revenue.
Accurate and Timely Issuance: ● Prompt Generation: Invoices should be issued within the prescribed time limit post-service delivery. ● Accuracy in Details: Ensuring accuracy in the invoicing details to avoid discrepancies.
Digital Adaptation: ● E-invoicing Option: Leveraging digital platforms for creating, sending, and storing invoices. ● Technology Integration: Incorporating invoicing software for efficiency and compliance.
Under Rule 53 of the CGST Act, 2017, a revised GST invoice can be issued for amendments to previously issued invoices. This revision could be either a decrease or an increase in the price of goods or services, affecting the applicable CGST/SGST/IGST rates.
 Marking of 'Revised Invoice':
Marking of 'Revised Invoice':
It is crucial to clearly mark the document as a 'Revised Invoice.'
 Supplier's Details:
Supplier's Details:
GSTIN, name, and address of the supplier must be included.
 Document Issue Date:
Document Issue Date:
The date on which the revised invoice is issued should be specified.
 Nature of the Document:
Nature of the Document:
The document must clearly state its purpose and nature.
 Recipient Details:
Recipient Details:
Includes name, GSTIN/UIN, and address of the registered recipient.
 Reference to Original Invoice:
Reference to Original Invoice:
Date and serial number of the corresponding original GST invoice should be mentioned.
 Shipping Address and Details:
Shipping Address and Details:
Detailed information about the shipping address is necessary.
 Unique Serial Number:
Unique Serial Number:
A distinct and sequential serial number, not exceeding 16 characters, must be assigned to each revised invoice.
 Authorisation:
Authorisation:
The invoice should be signed by the issuer or an authorized representative.

In certain scenarios, a supplier under the GST regime may not be required to issue a tax invoice. Understanding these scenarios helps businesses comply with GST regulations while also accommodating customer preferences.
If the recipient of the goods or services is not registered under GST, the supplier is not mandated to issue a GST invoice.
In cases where the recipient explicitly states that they do not require a GST invoice, the supplier is exempted from issuing one.
The supplier must ensure that not issuing a tax invoice is in compliance with GST laws and does not evade legal requirements of documentation under GST.
● A registered supplier has the option to issue a consolidated tax invoice at the end of each day for all the supplies made to unregistered recipients, where individual tax invoices were not issued.
Understanding when a tax invoice is not mandatory allows businesses to streamline their billing process. However, it's crucial to maintain proper records and documentation to ensure compliance with GST regulations and to facilitate smooth financial audits.
Adhering to the timelines set by the Indian Government for issuing GST invoices is crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring smooth business operations. Here's a breakdown of the timelines based on the type of supply:
● Goods suppliers must prepare the invoice on or before the date of goods removal. ● According to Section 2 (96) of the CGST Act, 2017, removal means dispatching or collecting goods by the recipient or an authorized person.
Suppliers can issue a GST invoice before payment or generating an account statement if there's a consistent business order with the recipient. This practice allows for efficient invoicing & ensuring timely documentation and streamlined processes.
● For services rendered, suppliers must issue the GST invoice within 30 days of service delivery. ● With Sleek Bill, effortlessly meet GST deadlines. Our software automates invoice generation and sends timely reminders for compliance.
Navigating the GST invoice issuance timelines can be complex, but with the right tools and knowledge, it's manageable. Sleek Bill is designed to assist businesses in adhering to these legal requirements seamlessly, ensuring that your focus remains on growing your business, not just on compliance.
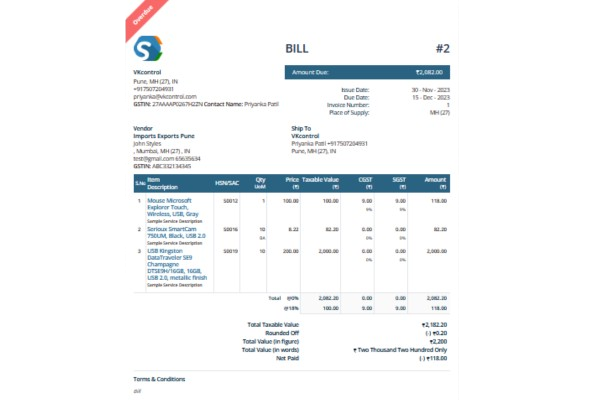
In the realm of goods supply under GST, creating multiple copies of invoices is mandatory for ensuring transparency and facilitating smooth transactions. Here's a guide to the copies required and their specific purposes:
Original Copy:
For the Recipient: ● The original copy of the GST invoice is issued to the recipient of the goods. ● It serves as the primary document for the buyer, confirming the transaction details.
Duplicate Copy
For Transporters: ● This copy is specifically for the transporter or the person responsible for the delivery of the goods. ● enabling transporters to verify and carry the goods from the supplier to the recipient.
Triplicate Copy
For the Supplier: ● The triplicate copy is retained by the supplier. ● It acts as a record for the supplier, documenting the goods supplied and ensuring traceability.
Utilize Sleek Bill to effortlessly manage these multiple invoice copies. Our software streamlines the creation and distribution of original, duplicate, and triplicate invoices, ensuring each party involved in the goods supply chain receives


*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
In the realm of GST (Goods and Services Tax), understanding the different types of invoices is crucial for compliance and accurate tax reporting. A prominent category under GST invoices is the "Bill of Supply."

Key Characteristics:
Tax Component: Unlike a standard GST invoice, a Bill of Supply does not contain a tax amount because the seller is not permitted to charge GST to the buyer.
Composition Scheme: It's commonly used by businesses that have opted for the GST Composition Scheme where they pay tax at a fixed rate on their turnover without charging GST to their customers.
Exempted Goods and Services: For supplies of goods and services that are exempt from GST, a Bill of Supply is issued instead of a regular tax invoice.

Nature and Purpose:
The Bill of Supply is an invoice format used when GST cannot be charged on the sale of goods or services. This typically applies to suppliers registered under the GST Composition Scheme and for certain exempted goods and services.
Compliance and Record-Keeping
Issuing a Bill of Supply is necessary for maintaining compliance with GST laws for eligible businesses. It serves as a key document for accounting and audit purposes.

Mandatory Details:
The Bill of Supply must include essential details like the supplier’s name, address, GSTIN, date of issue, description of goods or services, value of the supply, and a declaration stating eligibility for composition levy, if applicable.

Importance for Businesses
Understanding when to issue a Bill of Supply is critical for businesses to ensure GST compliance. It helps in accurate financial reporting and avoiding penalties related to GST violations. Businesses should familiarize themselves with the criteria and scenarios necessitating a Bill of Supply to streamline their billing processes and maintain transparent records.

Suitable for scenarios where the total value of multiple invoices for an unregistered buyer is less than INR 200. It's an efficient way to consolidate small-value transactions.

● Consolidation: Allows the seller to issue one collective invoice at the end of the day for multiple sales. ● Benefit: Simplifies documentation, especially for businesses that deal with numerous low-value transactions daily.

● Even though individual invoices are small, the aggregate invoice ensures that all transactions are duly recorded and reported, maintaining GST compliance.

● Issuance: The seller issues a debit note when the amount payable by the buyer increases. This could be due to reasons like under-billing, return of goods, or post-sale price adjustments. ● Impact: It effectively increases the value of the original invoice and subsequently the tax liability.

● Issuance: Issued by the seller when the invoice value decreases, which can happen in cases of over-billing, goods return, or post-sale discounts. ● Impact: It reduces the invoice value and the associated tax liability.

● Both debit and credit notes must be accurately recorded and reported in GST returns to ensure proper adjustment of tax liabilities.
● Aggregate Invoice: Simplifies the billing process for small transactions, reducing paperwork and administrative burden. ● Debit/Credit Notes: Essential for adjusting the invoice values post-sale, ensuring accurate tax calculation and compliance with GST norms.
For businesses, understanding the usage and implications of aggregate invoices, debit notes, and credit notes is vital. These tools provide flexibility in transaction recording, help maintain accurate financial records, and ensure compliance with the GST framework.

● Also Known As: Often referred to as the final invoice. ● Usage: Commonly used by small businesses and professionals for various transactions.

● Customization: Its format can be adjusted according to the specific needs and requirements of a business. ● Versatility Ideal for businesses with diverse product ranges or services that require a more tailored invoicing approach.

● Captures essential transaction details, including descriptions, quantities, and prices. ● While it's comprehensive, it might not include specific tax details unless required.

● Issuance: Must be issued by businesses registered under GST for all taxable sales or supplies. ● Purpose: Enables GST-registered buyers to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC).

● Timeliness: Strict timelines for issuance. Non-compliance can lead to substantial penalties. ● Essential Contents: Includes detailed tax information such as taxable value, tax rate, and tax amount for each item.

● Signature Requirement: Must be signed or e-signed by the authorized signatory of the organization, ensuring its validity and authenticity.
● Standard Invoice: Offers flexibility for non-GST or diverse transactional needs, catering to the varied invoicing requirements of businesses. ● Tax Invoice: Critical for GST compliance, facilitating the proper claim of ITC, and maintaining transparent tax records.
Seamless Invoicing for Your Business Needs – Optimize with Confidence.


*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
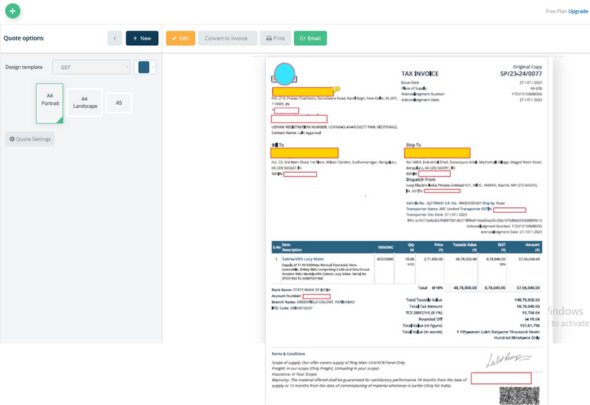

Digital Transformation in Invoicing:
Definition: An e-invoice is a GST-compliant digital invoice, authenticated by the GST Network (GSTN). Introduction: Implemented from 1st October 2020, aimed at standardizing the invoice process.

Combating Fake Invoicing:
Purpose: A government initiative to address fraudulent invoicing practices. Eligibility: Applicable to regular taxpayers under GST with an annual turnover above a specified threshold.

Process and Authenticity:
Verification: Validated through a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and a signed QR code via the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). Significance: Serves as a crucial and authoritative document for taxation purposes.
Preliminary Billing Document:
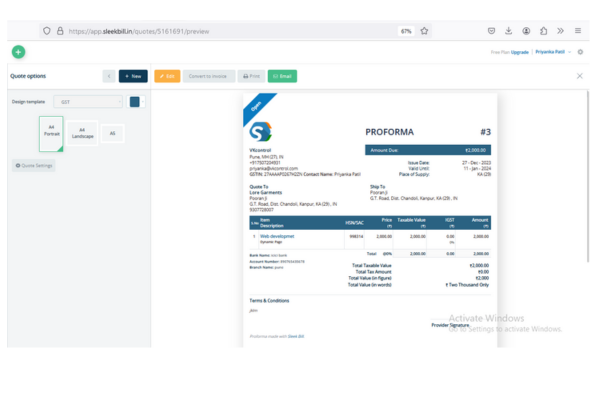
Definition: A provisional invoice that provides an estimated cost of products or services.
Role: Acts as an agreement to supply goods or services at an agreed price.
Pre-Sale Documentation:
Also Known As: Often referred to as an estimate or quotation. Usage: Issued before finalizing a sale, helping buyers understand potential costs.
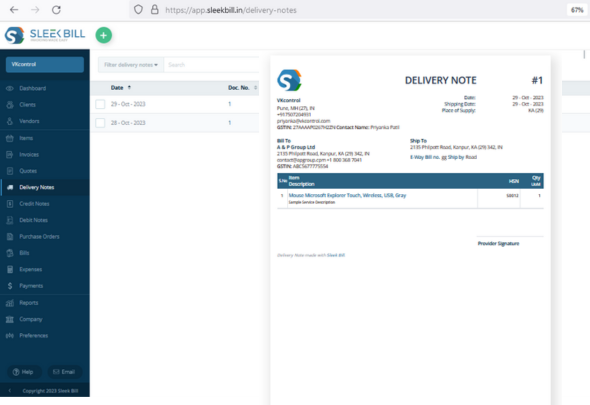
Shipment Documentation:
Purpose: Issued with the delivery of goods, confirming their receipt at the buyer's location. Contents: Details the list and quantity of delivered goods.

Handling Goods Discrepancies:
Damage Reporting: If goods are damaged, the delivery person notes it on behalf of the customer. Credit Note Issuance: A credit note may follow from the seller in case of discrepancies.

Record Keeping
Copies: Typically involves three copies - for the seller, transporter, and customer. Alternative Names: Also known as goods receipt notes or dispatch notes in some scenarios.
The Foundation of Goods Transportation

Mandatory for Transportation:
Requirement: Transporters must possess an e-way bill for moving goods exceeding a certain value. Scope: Applicable when transporting goods worth more than Rs.50,000, either per invoice or delivery challan.

Electronic Documentation:
Generation: Specific GST-registered sellers must generate this electronic waybill. Unique Identification: Upon generation, an E-way Bill Number (EBN) is assigned, serving as a unique identifier.
Access and Transparency:
Visibility: The e-way bill is accessible to the supplier, recipient, and transporter, ensuring transparency in the transportation process.
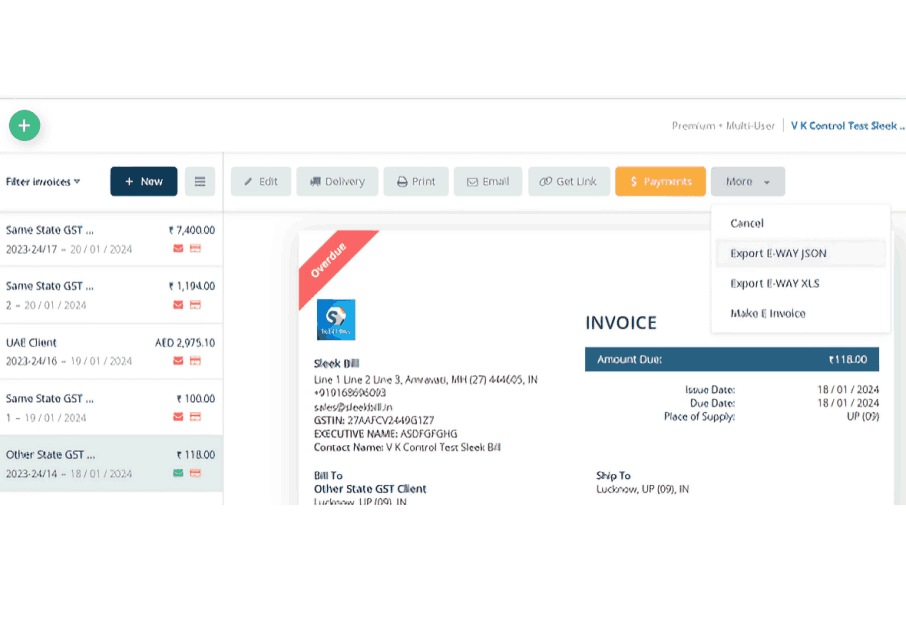

Prevention of Tax Evasion:
Objective:Designed to curb tax evasion by monitoring the movement of goods. Compliance: Ensures that goods being transported comply with GST norms.

Mandatory Details:
The Bill of Supply must include essential details like the supplier’s name, address, GSTIN, date of issue, description of goods or services, value of the supply, and a declaration stating eligibility for composition levy, if applicable.

Legal Implications:
Penalties: Non-compliance, such as transporting goods without a valid e-way bill, can lead to penalties and legal consequences. Verification: Authorities can verify the legitimacy of goods being transported through the e-way bill system.

Generating Process:
Online Platform: Generated through a dedicated portal, ensuring ease of access and use. Information Required: Includes details of the goods, consignor, consignee, transporter, and vehicle.

Integration with GST:
Linkage: Integrates with the GST framework, helping in the reconciliation of goods movement with GST returns. Tax Compliance: Assists in verifying tax compliance of goods in transit, aligning with GST regulations.
By understanding the nuances of the e-way bill, businesses can ensure seamless transportation of goods, while adhering to GST guidelines and minimizing compliance risks.