
A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses in India
*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST), introduced in India on July 1, 2017, marks a pivotal shift in the nation's fiscal framework. Here's a closer look at what GST entails and its impact:
Unified Tax System: GST stands as a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax, amalgamating various indirect taxes into one cohesive system. This integration simplifies the tax structure, making it more transparent and efficient.
Multi-Stage Nature: The term 'multi-stage' signifies that the tax is levied at every step of the production process, but is meant to be refunded to all parties in the various stages of production other than the final consumer.
Historical Context: GST's introduction on July 1, 2017, was a result of a long-standing need for tax reform. It replaced a complex web of taxes levied by the central and state governments, such as VAT, service tax, and excise.
Policy Evolution: The implementation of GST was a result of collaborative policymaking, involving consensus among India’s states and central government, aiming for a more unified economic landscape.
Consolidation of Indirect Taxes: GST's primary aim is to consolidate numerous indirect taxes under one umbrella, simplifying tax administration and reducing multiple tax layers.
Creating a Seamless National Market: By integrating various taxes, GST fosters a seamless national market, which enhances productivity and contributes to economic growth.
Enhancing Tax Efficiency: GST seeks to eliminate the cascading effect of taxes, a key feature that distinguishes it from the previous tax regime. This means that tax is not levied on tax, reducing the overall tax burden on consumers.
The Input Tax Credit (ITC) mechanism under GST allows businesses to claim credit for the tax paid on inputs used in the manufacturing or service delivery process.
Streamlining Tax Processes: GST represents a significant reform in the Indian tax system, streamlining and unifying the tax administration process. This reform has been instrumental in reducing complexity, improving compliance, and increasing government revenue.
Technology-Driven System: The implementation of GST brought with it a technology-driven framework. The GSTN (Goods and Services Tax Network) portal serves as a one-stop digital platform for tax registration, return filing, application for refunds, and other tax-related services.
Promoting Transparency and Compliance: By simplifying the tax structure and making processes transparent, GST encourages better compliance, thereby widening the tax base and reducing tax evasion.
Filing GST returns is a crucial part of tax compliance for businesses in India. Understanding the process can significantly simplify this mandatory task. Here's an overview of the GST return filing process, designed to provide clarity and ease for taxpayers:
-Login.png)
Accessing the GST Portal:
The first step involves registering on the official GST portal (gst.gov.in). This platform is the gateway for all GST-related activities.
Login Credentials:
After successful registration, businesses receive unique login credentials. These credentials are used to access their GST account on the portal.
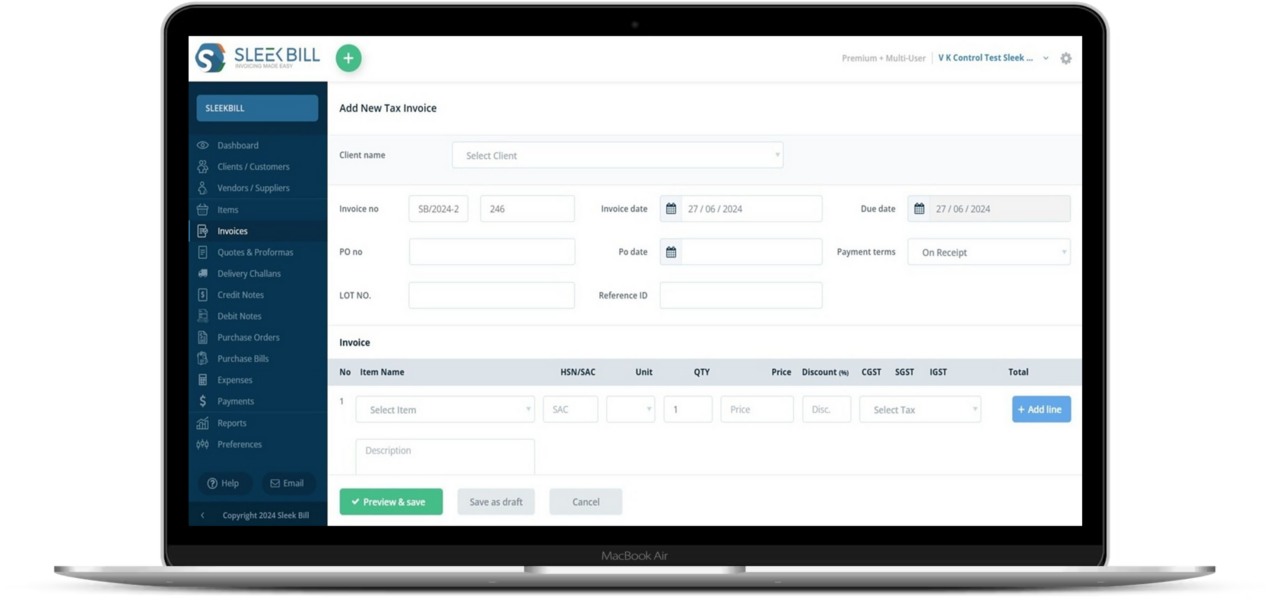
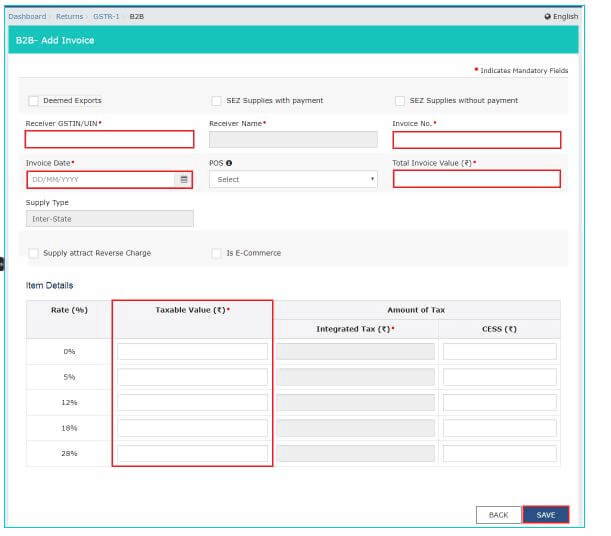
Uploading Invoices:
A critical component of the GST return filing is the upload of invoice details. This includes all sales (outward supplies) and purchase (inward supplies) invoices.
Accuracy in Details:
It's imperative to ensure accuracy while uploading invoice data, as these details form the basis of tax calculation and input tax credit.
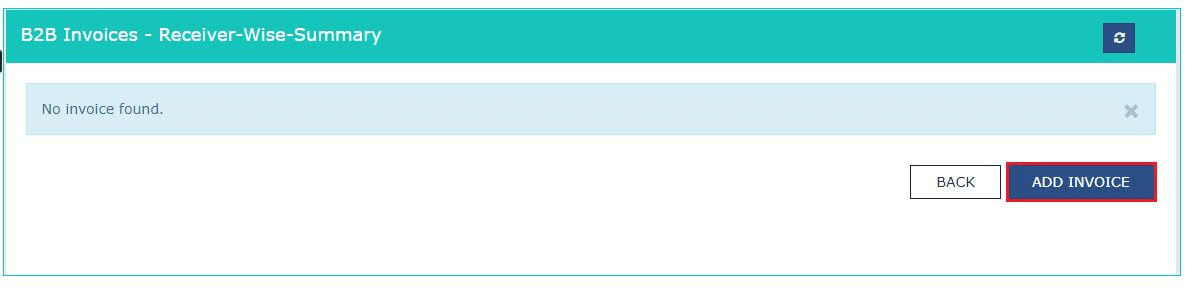
Types of Returns:
Businesses are required to file various types of returns, such as GSTR-1 for outward supplies, GSTR-2 for inward supplies, and GSTR-3B as a summary return.
Details of Sales and Purchases:
These returns should include comprehensive details of sales and purchases made during the return period.
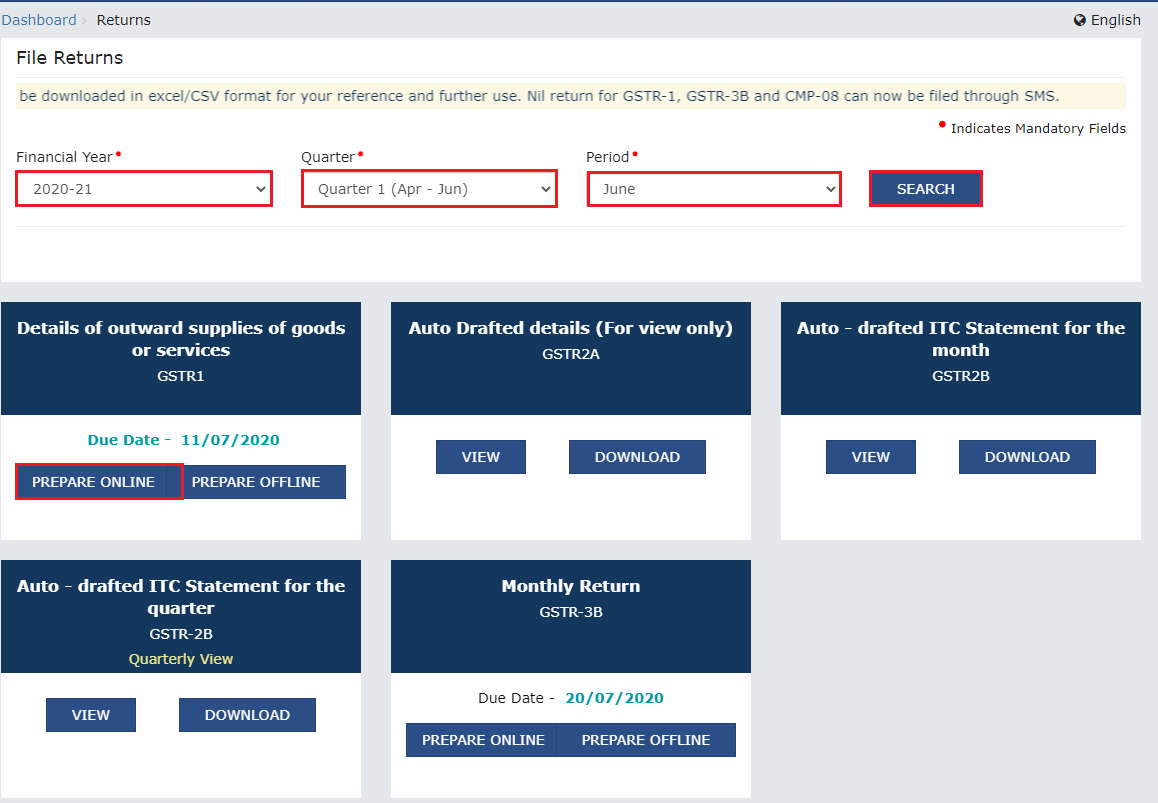
Digital Process:
The entire process of GST return filing is conducted online, making it convenient and efficient.
E-Filing Portal:
The GST portal provides an intuitive interface for filing returns. Taxpayers can fill in the requisite forms and upload necessary documents directly on the portal.
Review and Submission:
After filling in the details, review the return for any discrepancies. Once verified, submit the return on the portal.
Payment of Tax Liabilities:
These returns should include comprehensive details of sales and purchases made during the return period.
Boosting Tax Efficiency: One of the hallmark achievements of GST is the elimination of the cascading effect of taxes. Under the previous tax regime, taxes were imposed on an already taxed amount, leading to 'tax on tax'. GST eradicates this problem, ensuring a more equitable taxation process.
Input Tax Credit Mechanism: GST introduces the concept of Input Tax Credit, which allows businesses to reduce the taxes on outputs by the amount already paid on inputs, thereby reducing the overall tax burden.
Facilitating Easier Compliance: GST's unified approach has made compliance easier for businesses. The simplification of the tax structure has reduced the complexities involved in understanding and adhering to tax laws.
Better Governance: The GST framework promotes better governance by bringing transparency and accountability to tax administration. It has also led to an increase in the number of registered taxpayers, widening the tax base.
The GST framework in India mandates various types of returns to be filed by taxpayers at different intervals. Each return has its specific purpose and due date. Here's a comprehensive overview of the types of GST returns and their respective filing dates:
GSTR-1: Outward Supplies
Purpose: This return captures details of all outward supplies of goods and services.
Due Date: It needs to be filed by the 11th of the month following the tax period.
GSTR-2: Inward Supplies
Purpose: This return deals with the inward supplies of goods and services.
Due Date: The due date is the 15th of the month following the tax period. However, GSTR-2 is currently auto-populated and does not require active confirmation.
GSTR-4: Composition Scheme
Purpose: For taxpayers registered under the composition scheme, GSTR-4 simplifies the return process.
Filing Frequency: This return is filed on a quarterly basis.
GSTR-3: Monthly Return
Purpose: A comprehensive monthly return that consolidates the details of outward and inward supplies.
Due Date: It is filed by the 20th of the month following the tax period.
GSTR-9: Annual Return
Purpose: GSTR-9 is an annual return that consolidates the information provided in monthly/quarterly returns throughout the year.
Due Date: The deadline for filing GSTR-9 is December 31st of the next financial year.
GSTR-5: Non-Resident Taxpayers
Purpose: Specifically designed for non-resident foreign taxpayers.
Filing Frequency: GSTR-5 is filed monthly. It's important to note that this return is not applicable to Indian business owners.
Benefit for Consumers: With the removal of the cascading tax effect, GST has the potential to reduce the overall tax burden on consumers. This can lead to lower prices for various goods and services, benefiting the end consumer.
Impact on Businesses: The shift to GST has necessitated changes in business processes and accounting practices. Businesses are now adapting to the comprehensive and digitized processes that GST mandates, leading to more organized and efficient operations.
GSTN: A Digital Backbone: The Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) has been a game-changer in the digital transformation of India's tax system. This online portal facilitates all aspects of the GST process, including registration, filing of returns
The introduction of GST in India has brought about a significant change in tax compliance, particularly in the way businesses file their returns. Understanding the nuances of GST returns is pivotal for businesses to ensure they comply with the tax laws and maintain transparency. Here's a closer look at what GST returns entail:
The Essence of GST Returns
Periodic Filing Requirements: Excise invoices serve as a legal record of the sale of goods subject to excise tax, ensuring every transaction is transparently and accurately documented.
Comprehensive Transaction Records: These returns provide a detailed account of all transactions, encompassing sales, purchases, and the corresponding tax liabilities. They form the basis for tax assessment and validation.
Components of GST Returns
Sales and Purchases Details: GST returns include comprehensive data on all sales (outward supplies) and purchases (inward supplies) made by a business. This data is crucial for calculating the net tax liability.
Tax Payments and Input Tax Credit: The returns also detail the tax paid on purchases, enabling businesses to claim input tax credit. This credit is offset against the GST paid on sales, thereby reducing the overall tax liability.
Ensuring Compliance: Regular filing of GST returns is a legal obligation. It ensures that businesses comply with the GST laws and avoid penalties for non-compliance.
Facilitates Tax Calculation: GST returns play a pivotal role in the calculation of tax liabilities. They provide the necessary data for accurate tax computation, ensuring that businesses pay the correct amount of tax.
Transparency and Accountability: Filing GST returns promotes transparency and accountability in the tax system. It allows the government to keep track of transactions and ensures that businesses are paying their fair share of taxes.
Audit and Record-Keeping: The details provided in GST returns are essential for audit purposes. They help tax authorities in verifying the correctness of taxes paid and input tax credit claimed by businesses. This process is crucial for maintaining an accurate and transparent record of all taxable transactions.
Claiming Input Tax Credit: GST returns enable businesses to claim the input tax credit, which is a critical feature of the GST regime. By reporting their purchase details, businesses can offset their input tax against their output tax liability.
Verification of Credit Claims : The filing of returns by suppliers and recipients allows for cross-verification of input tax credit claims. This mechanism reduces the chances of tax evasion and ensures that only genuine credit claims are processed.
Adherence to Deadlines: Businesses must adhere to specific deadlines for filing GST returns. Timely submission is crucial to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Adaptation to Changes: The GST system is subject to periodic updates and changes. Businesses must stay informed and adapt their filing processes accordingly to remain compliant with the latest regulations.
Filing GST returns on time is crucial for maintaining compliance with tax laws. Late filing can lead to penalties, which are important for businesses to understand in order to avoid unnecessary charges. Here's what you need to know:
Nature of Penalty: Late filing of GST returns incurs a penalty termed as a 'late fee.'
Calculation Basis: This fee is calculated based on the delay duration, i.e., the number of days past the due filing date.
Varied Rates: The rate of late fees may differ based on the type of return and the duration of the delay.
Up-to-Date Awareness: It's crucial for taxpayers to stay informed about the current rates to assess the potential financial impact of delayed filing.
Financial Burden: Accumulating late fees can create a financial burden for businesses.
Compliance Record: Consistently late filings might affect the compliance rating and could lead to closer scrutiny by tax authorities.
Avoiding Additional Costs: Timely filing helps avoid these penalties, ensuring that businesses don't incur unnecessary expenses.
Adherence to Regulations: It also signifies adherence to GST regulations, which is essential for maintaining a good compliance record.
The Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) portal is a pivotal online platform that plays a key role in the facilitation and management of GST-related activities in India. Here's a guide on how taxpayers can leverage the GSTN portal for checking the status of their GST returns:
Central Hub: The GSTN portal serves as a central hub for all your GST-related activities.
Website Access: Taxpayers can access the portal by visiting the official GST website.
Login Credentials: Use your registered GST credentials to log in to the portal.
Dashboard Navigation: Once logged in, navigate to the 'Returns Dashboard.'
Status Overview: Here, you can view the status of each return filed, including whether it's been accepted, pending, or requires any modifications.
Real-Time Tracking: Check the real-time status of your GST filings, ensuring up-to-date compliance.
Transparency: This feature enhances transparency in your tax affairs, giving a clear picture of your tax liabilities and credits.
Record Keeping: The portal allows taxpayers to download their filed returns. This is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and for audit purposes.
Easy Access: Downloaded returns can be accessed anytime, providing a convenient way to keep track of past GST filings.
Effortlessly manage GST filing and ensure seamless adherence to tax regulations with Sleek Bill.


*Free & Easy - no hidden fees.