The introduction of electronic invoices (e-invoicing) is a modern technological development incorporated into the GST system, which makes the billing processes for entities and tax authorities very convenient too. Therefore, the e-invoice format schema as part of the e-invoicing system introduced on I st Oct 2020 shall provide direct input towards the GST compliant. This page discuss in detail, the structure, compulsory fields, and important aspects of the e-invoice format schema.
What is an E-Invoice Format Schema?
The e-invoice format schema is a predefined standard for creating GST-compliant e-invoices. It includes:
Mandatory Fields: Essential details required for the invoice to be valid under GST.
Optional Fields: Additional fields for specific business needs.
IRN (Invoice Reference Number): A unique identifier for every invoice, generated by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
Key Highlights
E-invoicing applies to businesses with turnover exceeding ₹5 crore from August 1, 2023.
Maximum number of line items per e-invoice: 1,000 (special cases up to 5,000 line items).
E-invoices are submitted to the IRP, validated, and assigned an IRN.
Structure of the E-Invoice Format Schema
The e-invoice format schema contains multiple sections and annexures, detailing all required information for compliance.
Mandatory Sections
-
1
Basic Details
Document type, date, and unique number.
-
2
Supplier Information
GSTIN, legal name, address, and contact details.
-
3
Recipient Information
GSTIN, legal name, address, and place of supply.
-
4
Invoice Item Details
Description, quantity, HSN code, and price of goods or services.
-
5
Document Total
Total taxable value, GST amounts (IGST, CGST, SGST), and total invoice value.
-
1
Invoice Item Details
Individual details for each line item, including discounts, unit price, and tax rates.
-
1
Document Total Details
Summary of total values and GST calculations.
Mandatory Sections
How is an E-Invoice Authorized?
Data Validation: The invoice data is validated by the IRP to ensure compliance.
Generation of IRN: The IRP generates a unique IRN using the supplier’s GSTIN, invoice number, and financial year.
Digital Signature and QR Code: The IRP assigns a digitally signed e-invoice and a QR code containing key invoice details.
Legal Compliance: An invoice without an IRN is considered invalid under GST law.

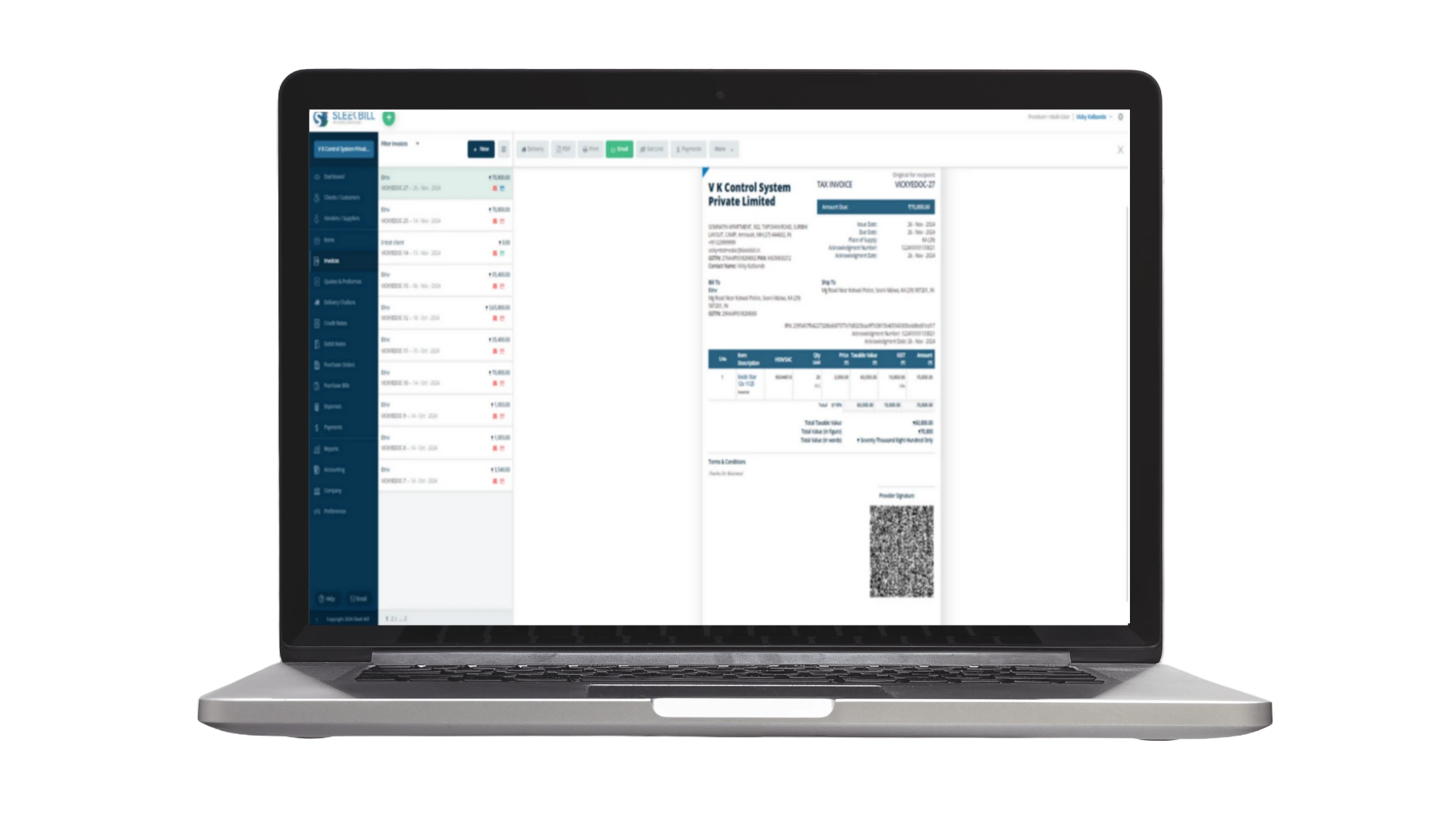




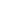
 GST Invoice Format
GST Invoice Format
 GST Billing Benefits
GST Billing Benefits







 Free training & support
Free training & support 60K Happy Customers Worldwide
60K Happy Customers Worldwide Serious about
Serious about